Multimer structure prediction
Overview
Teaching: 5 min
Exercises: 10 minQuestions
Objectives
Predict a multimeric complex with AlphaFold2.
Run multiple predictions in parallel.
Check that predicted interactions are consistent with our functional annotation.
Binding partners
In the canonical Type III secretion system, SctK is known to form direct interactions with SctD and SctQ.
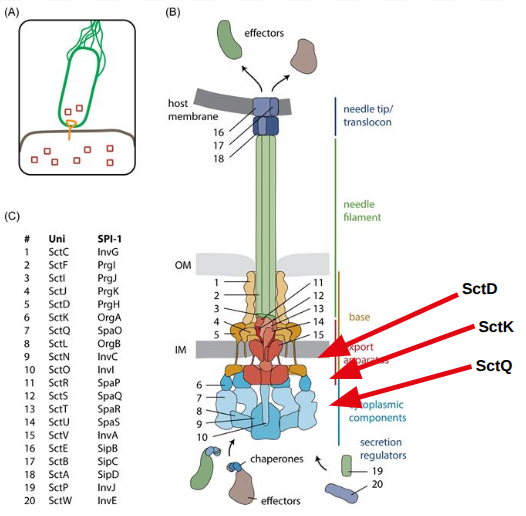
Available from: Samuel Wagner, Iwan Grin, Silke Malmsheimer, Nidhi Singh, Claudia E Torres-Vargas, Sibel Westerhausen, Bacterial type III secretion systems: a complex device for the delivery of bacterial effector proteins into eukaryotic host cells, FEMS Microbiology Letters, Volume 365, Issue 19, October 2018, fny201,
Can we identify the SctD and SctQ genes in our target genome?
Let’s view our assembly on the NCBI website and search for genes annotated as SctD and SctK.
SctD
gene complement(430545..432425) /gene="sctD" /locus_tag="PNK_0343" CDS complement(430545..432425) /gene="sctD" /locus_tag="PNK_0343" /function="FOG: FHA domain" /codon_start=1 /transl_table=11 /product="putative type III secretion system protein SctD" /protein_id="CUI15980.1" /translation="MVARLVAEEGDLKGLILSLENGDTWVIGRDPDECQLVIQDPLTS RKHLVARRTPEGISVENLSSTNPIQINEEEIGEQPRILQQGDTVKIGNEVFRYYTDTS AHVLDEGSPSEVKEPSEQTPIEIDDHPNPASAYPLHSQDRSESEEEKENDTIFDEDEE SFSPLAEINFGIAETGRWLLKVIGGPNNGAEFYMQAGHSYILGTDPHSCDIVFQDTSV SRQHAKIIVSPEDSLAIEDLKSRNGVLVSGAPVEGKQALIPSMIVTIGTTSFVVYDRE GEMQTIISPLLPSIVKVLQHEEEAPKIEEVPPPAPVEVEAAAATPPPEPAHHFGPYIL LAIIIGLFVLAGIGTTALFKSEPVVTLTQENAPELVQQALDSFPAVRHSYNKTSGNLL LLGHVRSQAEKNQLMYNLQGLKFIKNIDDSGIIIDEFVWREINSVLSKDPAWKGITIH SPEAGQFILSGYLETRKQAEQLSDYISVNFPYLDLLKKQVVVEEDVITQINVWLQTFN LRGVSAKIANGGEVTLSGNAPSDKAGEITQLIAKIKGISGVRLVNNYIKSEAPEMGIV NLSDRYEITGQSRLGTRYTVVINGRILSEGDSLDSMVITSIKPHAVFLEKDGTKYRID YK"
SctQ
gene complement(421992..423308) /gene="sctQ" /locus_tag="PNK_0334" CDS complement(421992..423308) /gene="sctQ" /locus_tag="PNK_0334" /function="Flagellar motor switch/type III secretory pathway protein" /codon_start=1 /transl_table=11 /product="putative type III secretion translocase SctQ" /protein_id="CUI15971.1" /translation="MTTPPTSYDWIRTIDPELKALDTIPLTGAAPSFPWADLSSRLAR SFDREGFSIQPKDIMWRTTDQLYDGLGDSPFPLIFAVPILKGDVCWVMPEQEMVLLET WLLTKESHPISFQDRALSESFYRFFALEVLYHLSQTSFDKSIAPILTNKTVLPQEDAL CLDISLSMHDQTLWGRLIISPDLRHSWVEHYASHGPSPLTQQMAQAVEVQVHLEAGKT QLSLAEWSAVSLGDFIVLDSCSLDADGSAGRVMLTVNGKAAHRGKIKDGNLKILELPL IQEVNPPPLQALNTPQEVPPPMAKHEDEDEDDLSDLDFTEDEELEDEESFDESLLNDE EEEKLSPPPAKPVKPEPSKVETSAKPVSETPYTPEHIPVALTVEVGRIQMTMENLLRL EPGNMLELNVHPEDGVDLTINGKLVGRGELLRIGENLGVRVLELGR"
Let’s see if our uncharacterised protein is predicted to form a high confidence interaction with either of these potential partners.
NOTE
To reduce the time required for prediction, we have trimmed the SctD and SctQ genes to the minimal region which would be expected to interact with a bona fide SctK gene.
Construct samplesheet
-
Navigate to the new working directory for this exercise
cd $MYSCRATCH/2025-ABACBS-workshop/exercises/exercise3/ -
Check that the FASTA files for the two target complexes are available in the
fasta/directory.cat fasta/SctD-complex.fastaOutput:
> PNK_0205 MDKRGWMMLRVFINCYNPKAGEALLKFLPQEEVQAVLSQDIRSTDLTPILYQPQKLLERMHYSWIEPLLGGFPEKLHPLVMAALTQEQISGLNPVIAPSTLSNPVKTFIINQLYTLLKADEHLPYDYLPETDLSPLGTWSKARLTELIDFLGLHDLASEMRHIVDKNQLKNIYTSLSSKQFYYLKVCLHQKEILSVPKLGIDPSKRDSTKLKRIVHRRGLLRLGKALCGQHPDFVWYLAHTLDTGRGKLILNAYQPESVPQVTSFLKGQVLNLMNFLKSE > SctD IAETGRWLLKVIGGPNNGAEFYMQAGHSYILGTDPHSCDIVFQDTSVSRQHAKIIVSPEDSLAIEDLKSRNGVLVSGAPVEGKQALIPSMIVTIGTTSFVVYDREGEMQTIISPcat fasta/SctQ-complex.fastaOutput:
> PNK_0205 MDKRGWMMLRVFINCYNPKAGEALLKFLPQEEVQAVLSQDIRSTDLTPILYQPQKLLERMHYSWIEPLLGGFPEKLHPLVMAALTQEQISGLNPVIAPSTLSNPVKTFIINQLYTLLKADEHLPYDYLPETDLSPLGTWSKARLTELIDFLGLHDLASEMRHIVDKNQLKNIYTSLSSKQFYYLKVCLHQKEILSVPKLGIDPSKRDSTKLKRIVHRRGLLRLGKALCGQHPDFVWYLAHTLDTGRGKLILNAYQPESVPQVTSFLKGQVLNLMNFLKSE > SctQ WADLSSRLARSFDREGFSIQPKDIMWRTTDQLYDGLGDSPFPLIFAVPILKGDVCWVMPEQEMVLLETWLLTKESHPISFQDRALSESFYRFFALEVLYHLSQTSFDKSIAPILTNKTVLPQEDALCLDISLSMHDQTLWGRLIISPDLRHSWVEHYASHGPSPL -
Confirm that the samplesheet in the working directory points to the FASTA files containing the proteins we want to predict.
cat samplesheet.csvOutput:
id,fasta pair1,fasta/SctD-complex.fasta pair2,fasta/SctQ-complex.fasta
Note
- Normally, AlphaFold2 generates predictions using 5 copies of the model which all output different predictions.
- In multimer mode, each of these 5 models is run with 5 independent replicates (5 x 5 = 25 total) and outputs are ranked by model confidence.
- Today, we are using a custom fork (
alphafold2_pred-single.sif) of AlphaFold2 which enables running only 1 of the 5 models.- We also provide an additional argument to run only a single replicate of this model (
-num_multimer_predictions_per_model=1).grep -A4 RUN_ALPHAFOLD2_PRED abacbs_profile-multimer.configOutput:
withName: 'RUN_ALPHAFOLD2_PRED' { container = '/scratch/references/abacbs2025/containers/alphafold2_pred-single.sif' ext.args = '--num_multimer_predictions_per_model=1' time = { 12.h } }
- These optimizations can reduce the GPU requirements by up to 25x for a small tradeoff in prediction quality.
- This could be important if we wish to scale to 1000s of predictions.
Predict multimers
- Execute the workflow using the script below:
nextflow run nf-core/proteinfold \ --input samplesheet.csv \ --outdir output \ --db /scratch/references/abacbs2025/databases/ \ --mode alphafold2 \ --alphafold2_model_preset multimer \ --use_gpu \ -c abacbs_profile-multimer.config \ --slurm_account $PAWSEY_PROJECT \ -r 53a1008 -
In our second terminal, check the status of the queue.
squeue --meJOBID USER ACCOUNT NAME EXEC_HOST ST REASON START_TIME END_TIME TIME_LEFT NODES PRIORITY QOS 34806314 tlitfin pawsey1017 nf-NFCORE_PROT nid002040 R None 09:16:39 21:16:39 11:59:37 1 75342 normal 34806313 tlitfin pawsey1017 nf-NFCORE_PROT nid002040 R None 09:16:37 21:16:37 11:59:35 1 75342 normalWe can see that multiple jobs have been initiated and are able to run in parallel. Nextflow can automatically distribute work across the available compute resources.
-
In our original terminal, wait for the MSA jobs to finish as indicated by the tick below.
[de/35e5fe] NFC…ALPHAFOLD2:RUN_ALPHAFOLD2_MSA (pair2) | 2 of 2 ✔ [fc/fb9ce4] NFC…LPHAFOLD2:RUN_ALPHAFOLD2_PRED (pair2) | 0 of 2 [- ] NFC…NFOLD:POST_PROCESSING:GENERATE_REPORT - [- ] NFC…E_PROTEINFOLD:POST_PROCESSING:MULTIQC - -
Before the pipeline is completed, cancel the execution by pressing
Ctrl+c.Interruptions
During long-running workflows, jobs can crash or be interrupted which can lead to lost progress.
Nextflow has the ability to resume workflow executions without repeating completed work.
-
Re-start our multimer predictions using the original command in combination with the
-resumeparameter.nextflow run nf-core/proteinfold \ --input samplesheet.csv \ --outdir output \ --db /scratch/references/abacbs2025/databases/ \ --mode alphafold2 \ --alphafold2_model_preset multimer \ --use_gpu \ -c abacbs_profile-multimer.config \ --slurm_account $PAWSEY_PROJECT \ -r 53a1008 \ -resume[54/a90051] NFC…ALPHAFOLD2:RUN_ALPHAFOLD2_MSA (pair1) | 2 of 2, cached: 2 ✔ [fc/fb9ce4] NFC…LPHAFOLD2:RUN_ALPHAFOLD2_PRED (pair1) | 0 of 2 [- ] NFC…NFOLD:POST_PROCESSING:GENERATE_REPORT - [- ] NFC…E_PROTEINFOLD:POST_PROCESSING:MULTIQC -We can see that Nextflow keeps track of completed tasks and continues from the latest checkpoint.
Execution timeline
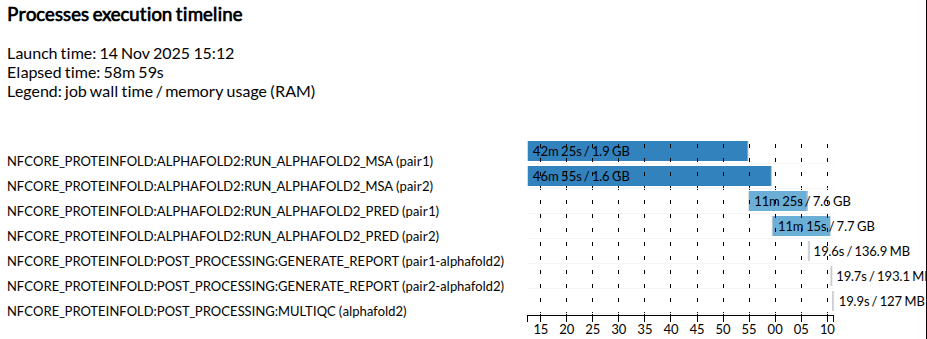
Observe in the full run that the 2 MSA jobs are executed in parallel.
Note that this will depend on the resources available when the workflow is being executed.
Results
After the workflow has completed, view the pair1_alphafold2_report.html file located in the output-multimer/generate/ directory.
You can find the file by navigating to the exercises/exercise3/output-multimer/generate/ directory in the VS-code file browser on the left-hand panel.
Right-click the pair1_alphafold2_report.html file and select Preview.
SctD
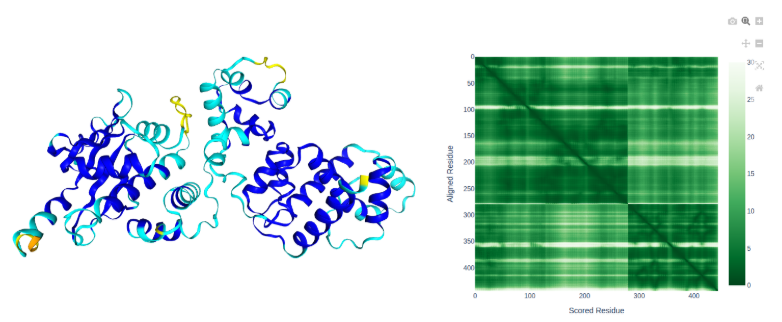
- Our uncharacterised protein forms a high confidence interaction with SctD
SctK
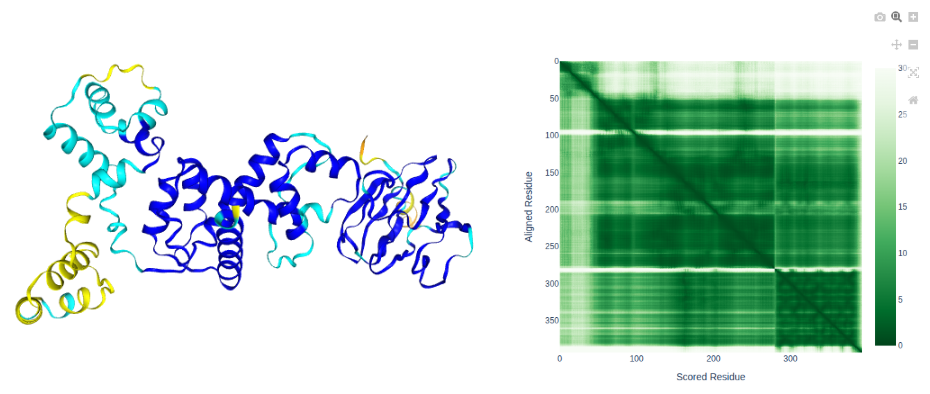
- Our uncharacterised protein forms a high confidence interaction with SctQ
Thought:
Can we screen for potential interactions systematically?
Key Points
Nextflow will distribute work over available resources.
Workflows can be resumed without re-doing completed tasks.